Cytokinetics Announces Primary Results from MAPLE-HCM Presented at the European Society of Cardiology Congress 2025 and Published in The New England Journal Of Medicine
Cytokinetics (NASDAQ:CYTK) announced positive Phase 3 results from MAPLE-HCM trial, comparing aficamten to metoprolol in patients with obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (oHCM). The study demonstrated aficamten's superiority over metoprolol across key metrics.
The trial's primary endpoint showed significant improvement in exercise capacity with aficamten (+1.1 mL/kg/min) compared to metoprolol (-1.2 mL/kg/min), with a difference of 2.3 mL/kg/min (p<0.0001). Notably, 51% of aficamten patients showed improved functional class versus 26% for metoprolol.
Aficamten demonstrated superiority in five of six secondary endpoints, including significant improvements in cardiac biomarkers and patient symptoms. The drug is currently under FDA review with a PDUFA date of December 26, 2025.
Cytokinetics (NASDAQ:CYTK) ha annunciato risultati positivi di Fase 3 dallo studio MAPLE-HCM, confrontando aficamten con metoprololo in pazienti con cardiomiopatia ipertrofica ostruttiva (oHCM). Lo studio ha dimostrato la superiorità di aficamten rispetto al metoprololo su metriche chiave.
L'endpoint primario ha mostrato un miglioramento significativo della capacità di esercizio con aficamten (+1,1 mL/kg/min) rispetto al metoprololo (-1,2 mL/kg/min), con una differenza di 2,3 mL/kg/min (p<0,0001). In particolare, il 51% dei pazienti trattati con aficamten ha riportato un miglioramento della classe funzionale rispetto al 26% con metoprololo.
Aficamten ha mostrato superiorità in cinque dei sei endpoint secondari, inclusi miglioramenti significativi nei biomarcatori cardiaci e nei sintomi riferiti dai pazienti. Il farmaco è attualmente in revisione FDA con data PDUFA del 26 dicembre 2025.
Cytokinetics (NASDAQ:CYTK) anunció resultados positivos de fase 3 del ensayo MAPLE-HCM, comparando aficamten con metoprolol en pacientes con miocardiopatía hipertrófica obstructiva (oHCM). El estudio demostró la superioridad de aficamten sobre metoprolol en métricas clave.
El criterio de valoración primario mostró una mejora significativa en la capacidad de ejercicio con aficamten (+1,1 mL/kg/min) frente a metoprolol (-1,2 mL/kg/min), con una diferencia de 2,3 mL/kg/min (p<0,0001). Cabe destacar que el 51% de los pacientes con aficamten mejoraron su clase funcional frente al 26% con metoprolol.
Aficamten demostró superioridad en cinco de los seis endpoints secundarios, incluidos mejorías significativas en biomarcadores cardíacos y en los síntomas de los pacientes. El fármaco está actualmente en revisión por la FDA con fecha PDUFA del 26 de diciembre de 2025.
Cytokinetics (NASDAQ:CYTK)�� 폐쇄�� 비후�� 심근병증(oHCM) 환자에서 아피캄텐�� 메토프로롤과 비교�� MAPLE-HCM 3�� 시험�� 긍정�� 결과�� 발표했습니다. 연구�� 주요 지표에�� 아피캄텐�� 메토프로롤보�� 우수���� 입증했습니다.
1�� 유효�� 평가지표는 아피캄텐 투여군의 운동 능력�� 유의하게 개선됨을 보여주었습니��(아피캄텐 +1.1 mL/kg/min vs 메토프로�� -1.2 mL/kg/min), 차이 2.3 mL/kg/min (p<0.0001). 특히 아피캄텐군의 51%가 기능�� 등급�� 개선�� 반면 메토프로롤군은 26%�� 그쳤습니��.
아피캄텐은 심장 바이오마�� �� 환자 증상�� 포함�� 6�� 보조 평가항목 �� 5개에�� 우수���� 보였습니��. �� 약물은 현재 FDA 심사 중이�� PDUFA 기한은 2025�� 12�� 26��입니��.
Cytokinetics (NASDAQ:CYTK) a annoncé des résultats positifs de phase 3 de l'essai MAPLE-HCM, comparant l'aficamten au métoprolol chez des patients atteints de cardiomyopathie hypertrophique obstructive (oHCM). L'étude a montré la supériorité de l'aficamten par rapport au métoprolol sur des paramètres clés.
Le critère d'évaluation principal a révélé une amélioration significative de la capacité d'exercice avec l'aficamten (+1,1 mL/kg/min) contre métoprolol (-1,2 mL/kg/min), avec une différence de 2,3 mL/kg/min (p<0,0001). Notamment, 51 % des patients traités par aficamten ont montré une amélioration de la classe fonctionnelle versus 26 % sous métoprolol.
L'aficamten a démontré sa supériorité sur cinq des six critères secondaires, incluant des améliorations significatives des biomarqueurs cardiaques et des symptômes rapportés par les patients. Le médicament est actuellement en revue par la FDA avec une date PDUFA au 26 décembre 2025.
Cytokinetics (NASDAQ:CYTK) gab positive Phase-3-Ergebnisse der MAPLE-HCM-Studie bekannt, in der aficamten mit Metoprolol bei Patienten mit obstruktiver hypertropher Kardiomyopathie (oHCM) verglichen wurde. Die Studie zeigte die Überlegenheit von aficamten gegenüber Metoprolol bei wichtigen Kennzahlen.
Der primäre Endpunkt zeigte eine signifikante Verbesserung der Belastungsfähigkeit mit aficamten (+1,1 mL/kg/min) gegenüber Metoprolol (-1,2 mL/kg/min), mit einer Differenz von 2,3 mL/kg/min (p<0,0001). Bemerkenswert ist, dass 51% der Patienten unter aficamten eine Verbesserung der Funktionsklasse zeigten gegenüber 26% unter Metoprolol.
Aficamten war in fünf von sechs sekundären Endpunkten überlegen, darunter deutliche Verbesserungen bei kardialen Biomarkern und patientenberichteten Symptomen. Das Medikament befindet sich derzeit in der FDA‑Prüfung mit einem PDUFA-Datum am 26. Dezember 2025.
- Primary endpoint met with statistical significance (p<0.0001) showing superiority over standard-of-care metoprolol
- 51% of aficamten patients showed functional class improvement vs 26% for metoprolol (p<0.001)
- Aficamten showed superiority in 5 of 6 secondary endpoints
- 81% reduction in NT-proBNP biomarker compared to metoprolol (p<0.0001)
- Similar overall adverse event rates between groups with lower down-titration rate for aficamten (4.5%) vs metoprolol (29.9%)
- One patient death reported in the aficamten group (69-year-old woman with multiple co-morbidities)
- Higher incidence of hypertension with aficamten (10.2%) compared to metoprolol (2.3%)
- No significant improvement in left ventricular mass index (LVMI) compared to metoprolol (p=0.16)
Insights
Aficamten demonstrated clear superiority over metoprolol in oHCM patients, positioning it to potentially transform first-line treatment for this condition.
The MAPLE-HCM trial results represent a significant advancement in the treatment of obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (oHCM). This Phase 3 randomized clinical trial directly compared Cytokinetics' cardiac myosin inhibitor aficamten against metoprolol, a beta-blocker that has been the standard first-line therapy for over 60 years.
The primary endpoint results are remarkably strong. Aficamten improved peak oxygen uptake (pVO2) by +1.1 mL/kg/min, while metoprolol actually reduced it by -1.2 mL/kg/min. This resulted in a significant between-group difference of 2.3 mL/kg/min (p<0.0001). This improvement in exercise capacity is clinically meaningful and demonstrates that aficamten not only prevents the exercise deterioration seen with beta-blockers but actually enhances functional capacity.
The secondary endpoints provide comprehensive evidence of aficamten's superiority. 51% of aficamten patients improved by ��1 NYHA functional class versus only 26% with metoprolol. Patient-reported symptoms measured by KCCQ-CSS showed significant improvements. Particularly striking were the hemodynamic improvements: aficamten significantly reduced left ventricular outflow tract gradients (LVOT-G) by 30-35 mmHg more than metoprolol and decreased NT-proBNP by 81%, indicating substantial reduction in cardiac wall stress.
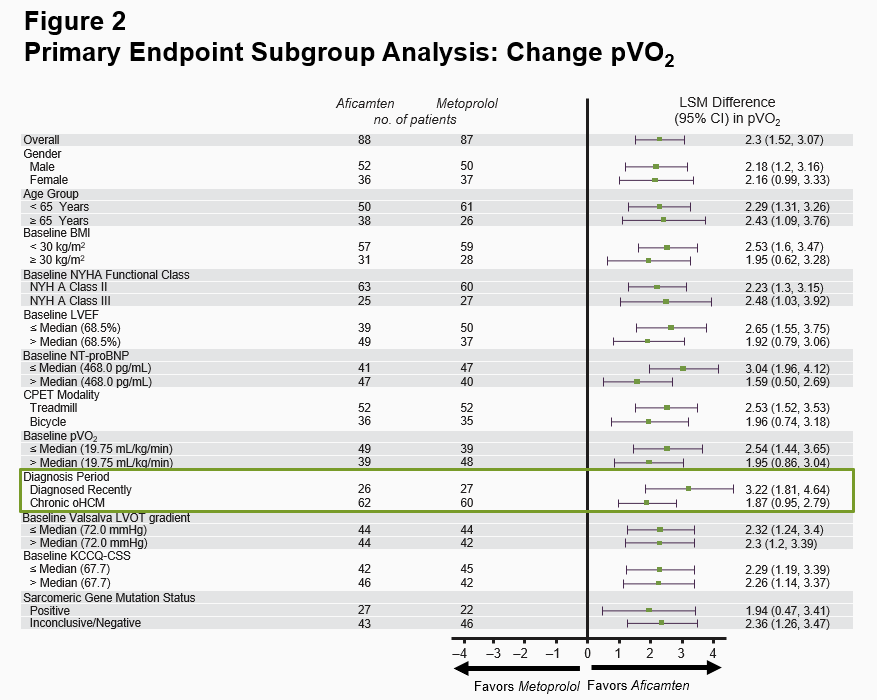
The safety profile appears manageable. While metoprolol required dose reduction in 29.9% of patients due to low blood pressure, low heart rate or other adverse events, aficamten needed down-titration in only 4.5% of patients. The consistent benefit across all subgroups, including newly diagnosed patients, suggests aficamten could potentially become first-line therapy for oHCM.
With an FDA decision expected by December 26, 2025, these results significantly strengthen aficamten's case for approval and could fundamentally change the treatment paradigm for oHCM by replacing beta-blockers as initial therapy.
Positive Trial Demonstrates Superiority of Aficamten to Standard-of-Care Beta-Blocker Metoprolol
Primary Endpoint Result Consistent Across All Prespecified Subgroups
Company to Host Investor Event and Webcast Tuesday September 2, 2025, at 8:00 AM Eastern Time
SOUTH SAN FRANCISCO, Calif., Aug. 30, 2025 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Cytokinetics, Incorporated (Nasdaq: CYTK) today announced that primary results from MAPLE-HCM (Metoprolol vs Aficamten in Patients with LVOT Obstruction on Exercise Capacity in HCM) were presented in a Hot Line Session at the European Society of Cardiology Congress 2025 in Madrid, Spain, and simultaneously published in The New England Journal of Medicine.1
MAPLE-HCM is a Phase 3 randomized, double-blind, active-comparator clinical trial of aficamten compared to metoprolol in patients with symptomatic obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (oHCM). MAPLE-HCM enrolled 175 patients, randomized on a 1:1 basis to receive aficamten or metoprolol as monotherapy. Compared to SEQUOIA-HCM, the pivotal Phase 3 clinical trial of aficamten, MAPLE-HCM was designed to include patients with less severe oHCM, enrolling patients without obstruction at rest and with higher predicted peak oxygen uptake (pVO2).
“This important study has the potential to inform our approach to treating obstructive HCM, as MAPLE-HCM provides the field its first look at a cardiac myosin inhibitor compared directly to a beta-blocker,�� said Pablo Garcia-Pavia, M.D., Ph.D., Head of the Inherited Cardiac Diseases and Heart Failure Unit, Department of Cardiology, Hospital Universitario Puerta de Hierro and Full Professor, Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares in Madrid, Spain. “In showing that aficamten is superior to metoprolol on all clinically relevant efficacy endpoints, these results call into question the reliance on beta-blockers as the initial treatment modality for obstructive HCM that has prevailed for over 60 years.��
“These results demonstrate that aficamten meaningfully improves exercise capacity in patients with obstructive HCM while treatment with metoprolol resulted in a meaningful reduction in exercise capacity,�� said Fady I. Malik, M.D., Ph.D., Cytokinetics�� Executive Vice President of Research & Development. “The clinical difference in the two treatments is reinforced by the effect of aficamten on the secondary endpoints. Compared to first-line standard-of-care metoprolol, treatment with aficamten had a larger effect on measures of symptoms, functional class, and LVOT gradients. Importantly, these effects were achieved in a broader patient population with oHCM than previously studied in SEQUOIA-HCM, inclusive of patients in MAPLE-HCM with less severe disease as measured by objective metrics of disease burden.��
Aficamten is an investigational drug candidate currently under regulatory review in the U.S; the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is reviewing a New Drug Application (NDA) for aficamten with a Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA) target action date of December 26, 2025.
Results of MAPLE-HCM
The primary endpoint in MAPLE-HCM was the mean change from baseline in pVO2 for aficamten compared to metoprolol after 24 weeks of treatment. For aficamten, the mean change in pVO2 from baseline to Week 24 was +1.1 mL/kg/min (
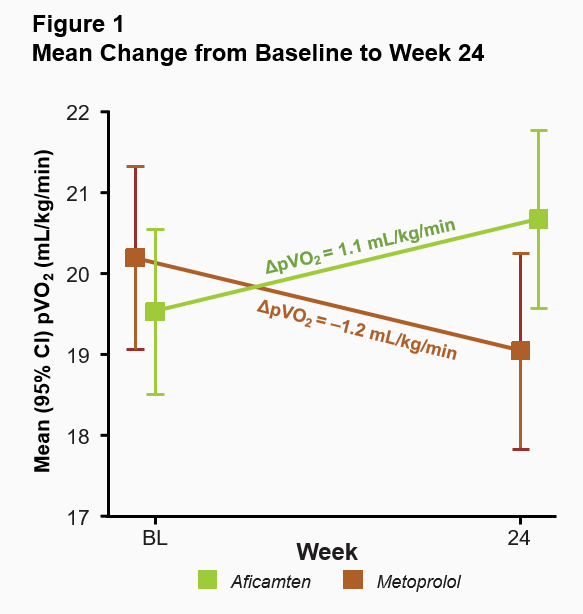
Aficamten also showed superiority to metoprolol in five of six secondary endpoints, all of which were evaluated at 24 weeks compared to baseline (Table 1). Aficamten substantially improved functional class and reduced patient symptom burden. For patients treated with aficamten,
| Table 1: Secondary Endpoints | |
| Endpoint | P-Value |
| Proportion of patients with ��1 class improvement in NYHA functional class from baseline to week 24 | P <0.001 |
| Change in KCCQ-CSS from baseline to week 24 | P <0.010 |
| Change in NT-proBNP from baseline to week 12 | P <0.001 |
| Change in post-Valsalva LVOT-G from baseline to week 24 | P <0.001 |
| Change from baseline to week 24 in LAVI | P <0.001 |
| Change from baseline to week 24 in LVMI | P = 0.16 |
Relative to metoprolol, aficamten significantly improved resting left ventricular outflow tract gradient (LVOT-G) (LSM difference = -30 mmHg; p<0.0001) and Valsalva LVOT-G (LSM difference = -35 mmHg; p<0.0001), with a modest reduction in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) (LSM difference = -
Compared to metoprolol, aficamten was associated with an
Overall, the rate of adverse events (AEs) was similar between groups. Aficamten was down-titrated in four patients (
Investor Webcast Information
Cytokinetics will host an investor webcast on September 2, 2025, at 8:30 AM Eastern Time to discuss the primary results from MAPLE-HCM and other data presented at the European Society of Cardiology Congress 2025. Interested parties can register online at . The live webcast will be available on the Investors & Media section of the Cytokinetics website at . A replay of the webcast will be archived on the Cytokinetics website for six months.
About Aficamten
Aficamten is an investigational selective, small molecule cardiac myosin inhibitor discovered following an extensive chemical optimization program that was conducted with careful attention to therapeutic index and pharmacokinetic properties.2 Aficamten was designed to reduce the number of active actin-myosin cross bridges during each cardiac cycle and consequently suppress the myocardial hypercontractility that is associated with HCM. In preclinical models, aficamten reduced myocardial contractility by binding directly to cardiac myosin at a distinct and selective allosteric binding site, thereby preventing myosin from entering a force producing state.
The development program for aficamten is assessing its potential as a treatment that improves exercise capacity as measured by peak oxygen uptake (pVO2) and relieves symptoms in patients with HCM. Aficamten was evaluated in SEQUOIA-HCM, a positive pivotal Phase 3 clinical trial in patients with symptomatic obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (oHCM). Aficamten received Breakthrough Therapy Designation for the treatment of symptomatic HCM from the U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA) and for the treatment of symptomatic obstructive HCM from the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) in China.
Aficamten is also currently being evaluated in ACACIA-HCM, a Phase 3 clinical trial of aficamten in patients with non-obstructive HCM; CEDAR-HCM, a clinical trial of aficamten in a pediatric population with oHCM; and FOREST-HCM, an open-label extension clinical study of aficamten in patients with HCM.
This communication contains a summary of new data related to the clinical development of aficamten presented at the European Society of Cardiology 2025 Congress. Aficamten is an investigational drug and is not approved by any regulatory agency. Its safety and efficacy have not been established. Aficamten is currently under regulatory review in the U.S, where the FDA is reviewing a New Drug Application (NDA) for aficamten with a Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA) target action date of December 26, 2025. Additionally, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) is reviewing a Marketing Authorization Application (MAA) for aficamten, and The Center for Drug Evaluation (CDE) of the China National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) is reviewing an NDA for aficamten with Priority Review.
About Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a disease in which the heart muscle (myocardium) becomes abnormally thick (hypertrophied). The thickening of cardiac muscle leads to the inside of the left ventricle becoming smaller and stiffer, and thus the ventricle becomes less able to relax and fill with blood. This ultimately limits the heart’s pumping function, resulting in reduced exercise capacity and symptoms including chest pain, dizziness, shortness of breath, or fainting during physical activity. HCM is the most common monogenic inherited cardiovascular disorder, with approximately 280,000 patients diagnosed, however, there are an estimated 400,000-800,000 additional patients who remain undiagnosed in the U.S.3,4,5 Two-thirds of patients with HCM have obstructive HCM (oHCM), where the thickening of the cardiac muscle leads to left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) obstruction, while one-third have non-obstructive HCM (nHCM), where blood flow isn’t impacted, but the heart muscle is still thickened. People with HCM are at high risk of also developing cardiovascular complications including atrial fibrillation, stroke and mitral valve disease.6 People with HCM are at risk for potentially fatal ventricular arrhythmias and it is one of the leading causes of sudden cardiac death in younger people or athletes.7 A subset of patients with HCM are at high risk of progressive disease leading to dilated cardiomyopathy and heart failure necessitating cardiac transplantation.
About Cytokinetics
Cytokinetics is a specialty cardiovascular biopharmaceutical company, building on its over 25 years of pioneering scientific innovations in muscle biology to advance a pipeline of potential new medicines for patients suffering from diseases of cardiac muscle dysfunction. Cytokinetics is readying for potential regulatory approvals and commercialization of aficamten, a cardiac myosin inhibitor following positive results from SEQUOIA-HCM, the pivotal Phase 3 clinical trial in patients with obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM). Aficamten is also being evaluated in additional clinical trials enrolling patients with obstructive and non-obstructive HCM. Cytokinetics is also developing omecamtiv mecarbil, a cardiac myosin activator, in patients with heart failure with severely reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), ulacamten, a cardiac myosin inhibitor with a mechanism of action distinct from aficamten, for the potential treatment of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) and CK-089, a fast skeletal muscle troponin activator with potential therapeutic application to a specific type of muscular dystrophy and other conditions of impaired skeletal muscle function.
For additional information about Cytokinetics, visit and follow us on , , and .
Forward-Looking Statements
This press release contains forward-looking statements for purposes of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 (the “Act��). Cytokinetics disclaims any intent or obligation to update these forward-looking statements and claims the protection of the Act’s Safe Harbor for forward-looking statements. Examples of such statements include, but are not limited to, statements express or implied relating to the properties, treatment effect or potential benefits of aficamten or any of our other drug candidates or our ability to obtain regulatory approval for aficamten for the treatment of obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy or any other indication from FDA or any other regulatory body in the United States or abroad by any particular date, if ever. Such statements are based on management’s current expectations, but actual results may differ materially due to various risks and uncertainties, including, but not limited to the risks related to Cytokinetics�� business outlines in Cytokinetics�� filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission. Forward-looking statements are not guarantees of future performance, and Cytokinetics�� actual results of operations, financial condition and liquidity, and the development of the industry in which it operates, may differ materially from the forward-looking statements contained in this press release. Any forward-looking statements that Cytokinetics makes in this press release speak only as of the date of this press release. Cytokinetics assumes no obligation to update its forward-looking statements whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, after the date of this press release.
CYTOKINETICS® and the CYTOKINETICS and C-shaped logo are registered trademarks of Cytokinetics in the U.S. and certain other countries.
Contact:
Cytokinetics
Diane Weiser
Senior Vice President, Corporate Affairs
(415) 290-7757
References:
- Garcia-Pavia, P, et al. Aficamten or Metoprolol Monotherapy for Obstructive Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 2025
- Chuang C, Collibee S, Ashcraft L, et al. Discovery of Aficamten (CK-274), a Next-Generation Cardiac Myosin Inhibitor for the Treatment of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. J Med Chem. 2021;64(19):14142��14152. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c01290
- CVrg: Heart Failure 2020-2029, p 44; Maron et al. 2013 DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60397-3; Maron et al 2018 10.1056/NEJMra1710575
- Symphony Health 2016-2021 Patient Claims Data DoF;
- Maron MS, Hellawell JL, Lucove JC, Farzaneh-Far R, Olivotto I. Occurrence of Clinically Diagnosed Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy in the United States. Am J Cardiol. 2016; 15;117(10):1651-1654.
- Gersh, B.J., Maron, B.J., Bonow, R.O., Dearani, J.A., Fifer, M.A., Link, M.S., et al. 2011 ACCF/AHA guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. Journal of the American College of Cardiology and Circulation, 58, e212-260.
- Hong Y, Su WW, Li X. Risk factors of sudden cardiac death in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Current Opinion in Cardiology. 2022 Jan 1;37(1):15-21
Photos accompanying this announcement are available at:









